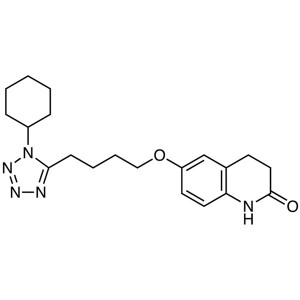
Cilostazol CAS 73963-72-1 Assay 98.0~102.0% API USP Standard
Ruifu Chemical is the leading supplier of Cilostazol (CAS: 73963-72-1) with high quality, can meet the USP / EP / JP standard. Ruifu Chemical has been supplying APIs and pharmaceutical intermediates more than 15 years.
Ruifu Chemical can provide worldwide delivery, competitive price, excellent service.
Purchase Cilostazol, please contact us by e-mail: alvin@ruifuchem.com
| Chemical Name | Cilostazol |
| Synonyms | OPC-13013; OPC13013; OPC 13013; Pletal; Pletaal; Cilostazole; 6-[4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy]-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-quinolinone |
| Stock Status | In Stock, Commercial Production |
| CAS Number | 73963-72-1 |
| Molecular Formula | C20H27N5O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 369.46 g/mol |
| Melting Point | 158.0 to 162.0℃ |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in Water |
| Solubility | Slightly Soluble in Methanol. Insoluble in Ether |
| COA & MSDS | Available |
| Sample | Available |
| Origin of Product | Shanghai, China |
| Product Categories |
API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) |
| Brand | Ruifu Chemical |
| Items | Specifications | Results |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder | White crystalline powder |
| Solubility | It is slightly soluble in methanol, in ethanol (99.5), in acetonitrile, and practically insoluble in water. |
Conforms |
| Identification A. | The IR spectrum should correspond to that obtained with RS | Conforms |
| Identification B. | The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation should correspond to that in the chromatogram of the RS, as obtained in the Assay | Conforms |
| Loss on Drying | ≤0.25% | 0.07% |
| Residue on Ignition | ≤0.10% | 0.04% |
| Chloride | ≤180 ppm | <180ppm |
| Heavy Metals | ≤0.001% | <0.001% |
| Particle Size | 90% less than 20μm and 10% less than 10μm | Conforms |
| Related Compounds | ||
| Impurity A | ≤0.10% | 0.02% |
| Impurity B | ≤0.10% | Not Detected |
| Impurity C | ≤0.10% | 0.03% |
| Any Other Individual Impurity | ≤0.10% | Conforms |
| Total Impurities | ≤0.40% | 0.21% |
| Residual Solvents | ||
| N,N-Dimethylacetamide | ≤1090 ppm | Conforms |
| Chloroform | ≤60 ppm | 25 ppm |
| Methanol | ≤3000 ppm | 950 ppm |
| Assay by HPLC | 98.0% ~ 102.0% (calculated on dried basis) | 99.8% |
| Microbiological Test | ||
| Total Aerobic Microbial Count | ≤1000 cfu | Conforms |
| Total Moulds & Yeasts | ≤1000 cfu | Conforms |
| E.Coli | Absent | Conforms |
| Salmonella | Absent | Conforms |
| Conclusion | The product has been tested and complies with the USP38 specifications | |
Package: Bottle, Aluminium foil bag, 25kg/cardboard drum, or according to customer's requirement.
Storage Condition: Keep the container tightly closed. Store in a cool, dry (2-15℃) and well-ventilated warehouse away from incompatible substances. Keep away from sunshine; avoid fire and heat sources; avoid moisture.
Shipping: Deliver to worldwide by air, by sea, by FedEx / DHL Express. Provide fast and reliable delivery.
Cilostazol
C20H27N5O2 369.46
2(1H)-Quinolinone, 6-[4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy]-3,4-dihydro-.
6-[4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy]-3,4-dihydrocarbostyril [73963-72-1]; UNII: N7Z035406B.
» Cilostazol contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of C20H27N5O2, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage-Preserve in tight containers, and store at room temperature.
USP REFERENCE STANDARDS <11>-
USP Cilostazol RS
USP Cilostazol Related Compound A RS
6-Hydroxy-3,4-dihydro-1H-quinolin-2-one.
C9H9NO2 163.17
USP Cilostazol Related Compound B RS
6-[4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-butoxy]-1H-quinolin-2-one.
C20H25N5O2 367.45
USP Cilostazol Related Compound C RS
1-(4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butyl)-6-(4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one.
C31H45N9O2 575.75
Identification-
Change to read:
A: Spectroscopic Identification Tests <197>, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K (CN 1-May-2020).
B: The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.
Loss on drying <731>-Dry it at 110° for 3 hours: it loses not more than 0.3% of its weight.
Residue on ignition <281>: not more than 0.1%.
Chloride <221>-
Test solution-Dissolve 0.5 g of Cilostazol in 40 mL of dimethylformamide, add 6 mL of diluted nitric acid and dimethylformamide to make 50 mL.
Control solution-To 0.25 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid add 6 mL of diluted nitric acid and dimethylformamide to make 50 mL.
Procedure-Add 1 mL of silver nitrate TS to the Test solution and to the Control solution, mix well, and allow to stand for 5 minutes, protecting from direct sunlight. Compare the opalescence developed in both solutions against a black background by viewing downward or transversely. The opalescence developed in the Test solution is not more than that of the Control solution (0.018%).
Related compounds-
Diluent, Solution A, Solution B, Mobile phase, System suitability solution, and Chromatographic system-Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution-Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Cilostazol RS and USP Cilostazol Related Compound C RS in acetonitrile, with sonication if necessary, to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 0.5 mg per mL of each component. Transfer 4 mL of this solution to a 10-mL volumetric §ask, and dilute with water to volume. Further dilute this solution, stepwise if necessary, with Diluent to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 0.4 µg per mL of each component.
Test solution-Transfer about 20 mg of Cilostazol, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric §ask, dissolve in 20 mL of acetonitrile, with sonication if necessary. Dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Procedure-Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of cilostazol related compound C by the formula:
0.1(Cs /CT )(ru /rs )
in which Cs is the concentration, in µg per mL, of cilostazol related compound C in the Standard solution; CT is the concentration, in mg
per mL, of Cilostazol in the Test solution; ru is the peak response for cilostazol related compound C obtained from the Test solution;
and rs is the peak response for cilostazol related compound C obtained from the Standard solution. Calculate the percentage of other
impurities by the formula:
0.1(1/F)(Cs /CT )(ru/rs )
in which F is the relative response factor from Table 1; Cs is the concentration, in µg per mL, of cilostazol in the Standard solution; CT is
the concentration, in mg per mL, of cilostazol in the Test solution; ru is the peak response for any other impurity obtained from the Test
solution; and rs is the peak response for cilostazol obtained from the Standard solution.
Table 1
Name Relative Retention Time Relative Response Factor (F) Limit (%)
Cilostazol related compound A 0.2 1.7 0.1
Cilostazol related compound B 0.9 0.58 0.1
Cilostazol 1.0 1.0 -
Cilostazol related compound C 1.9 - 0.1
Any other individual impurity - 1.0 0.1
1 6-Hydroxy-3,4-dihydro-1H-quinolin-2-one
2 6-[4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-butoxy]-1H-quinolin-2-one
3 1-(4-(5-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-1-yl)butyl)-6-(4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one
In addition to not exceeding the limits for impurities in Table 1, not more than 0.4% of total impurities is found.
Assay-
Diluent-Use a mixture of water and acetonitrile (60:40).
Solution A-Use a mixture of water and acetonitrile (70:30).
Solution B-Use a mixture of water and acetonitrile (50:50).
Mobile phase-Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if
necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography <621>).
System suitability solution-Prepare a solution in Diluent having known concentrations of about 0.05 mg per mL each of USP Cilostazol
RS, USP Cilostazol Related Compound A RS, and USP Cilostazol Related Compound B RS.
Standard preparation—Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Cilostazol RS in acetonitrile, with sonication if necessary, to
obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1.0 mg per mL. Transfer 4 mL of this solution to a 10-mL volumetric §ask,
and dilute with water to volume. Further dilute this solution with Diluent to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about
0.04 mg per mL.
Assay preparation-Transfer about 20 mg of Cilostazol, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in 20 mL of acetonitrile, sonicate if necessary, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 1 mL of this solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Diluent to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see CHROMATOGRAPHY <621>)-The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 254-nm detector and a 4.6-mm ×
10-cm column that contains 3.5-µm packing L7. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. The column temperature is maintained at 40°. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Time (minutes) Solution A (%) Solution B (%) Elution
0–6.5 100→50 0→50 linear gradient
6.5–10 50→0 50→100 linear gradient
10–20 0 100 isocratic
20–20.1 0→100 100→0 linear gradient
20.1–28 100 0 re-equilibration
Chromatograph the System suitability solution, identify the components using Table 1, and record the peak responses as directed for
Procedure: the resolution, R, between cilostazol related compound B and cilostazol is not less than 3.0; the tailing factor for the cilostazol peak is not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure-Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of
C20H27N5O2 in the portion of Cilostazol taken by the formula:
500C(ru /rs )
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of cilostazol in the Standard preparation; and ru and rs are the peak responses obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
How to Purchase? Please contact Dr. Alvin Huang: sales@ruifuchem.com or alvin@ruifuchem.com
15 Years Experience? We have more than 15 years of experience in the manufacture and export of a wide range of high quality pharmaceutical intermediates or fine chemicals.
Main Markets? Sell to domestic market, North America, Europe, India, Korea, Japanese, Australia, etc.
Advantages? Superior quality, affordable price, professional services and technical support, fast delivery.
Quality Assurance? Strict quality control system. Professional equipment for analysis include NMR, LC-MS, GC, HPLC, ICP-MS, UV, IR, OR, K.F, ROI, LOD, MP, Clarity, Solubility, Microbial limit test, etc.
Samples? Most products provide free samples for quality evaluation, shipping cost should be paid by customers.
Factory Audit? Factory audit welcome. Please make an appointment in advance.
MOQ? No MOQ. Small order is acceptable.
Delivery Time? If within stock, three days delivery guaranteed.
Transportation? By Express (FedEx, DHL), by Air, by Sea.
Documents? After sales service: COA, MOA, ROS, MSDS, etc. can be provided.
Custom Synthesis? Can provide custom synthesis services to best fit your research needs.
Payment Terms? Proforma invoice will be sent first after confirmation of order, enclosed our bank information. Payment by T/T (Telex Transfer), PayPal, Western Union, etc.
| Hazard Symbols | Xi - Irritant |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | VC8277500 |
| HS Code | 2933 9900.92 |
Cilostazol (CAS: 73963-72-1) is developed by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Company, Japan, launched in 1988. It has vasodilator effect and antiplatelet function, and increases the concentration of cAMP in platelets and smooth muscle by inhibiting the activity of phosphodiesterase in platelets and vascular smooth muscle, and exerts antiplatelet effect and vasodilator effect. Inhibition of ADP, epinephrine, collagen and arachidonic acid-induced platelet aggregation and release in the early and second phase, the model of cerebral circulation and peripheral circulation disorder caused by sodium laurate has obvious antithrombotic effect. It can be used to treat chronic arterial occlusive disease caused by atherosclerosis, Takayasu arteritis, Thromboangiitis obliterans, diabetes, etc.
-
Cilostazol CAS 73963-72-1 Assay 98.0~102.0% API...
-
Captopril CAS 62571-86-2 API Factory USP High Q...
-
Cefotiam Hydrochloride CAS 66309-69-1 API USP S...
-
Cholestyramine CAS 11041-12-6 USP API Factory H...
-
Doxorubicin Hydrochloride CAS 25316-40-9 API US...
-
Gemcitabine Hydrochloride CAS 122111-03-9 API U...
-
Guanfacine Hydrochloride Guanfacine HCl CAS 291...
-
Adenosine CAS 58-61-7 Assay 99.0%-101.0% USP St...
-
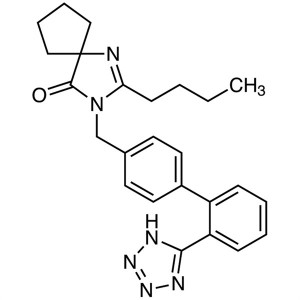
Irbesartan CAS 138402-11-6 Assay 98.0~102.0% (H...
-
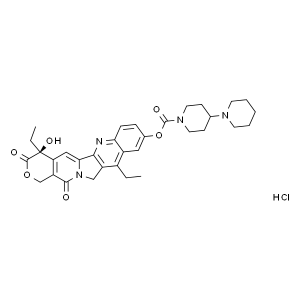
Irinotecan Hydrochloride CAS 100286-90-6 Purity...
-
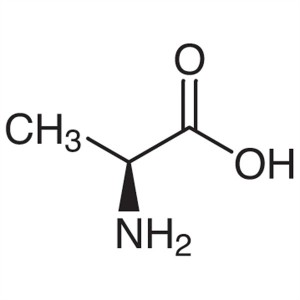
L-Alanine CAS 56-41-7 (H-Ala-OH) Purity 98.5%~1...
-
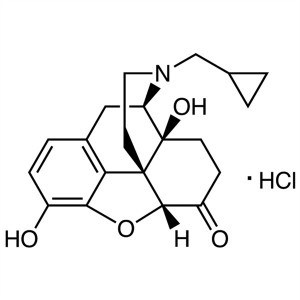
Naltrexone Hydrochloride CAS 16676-29-2 API USP...
-
Noscapine Hydrochloride Hydrate CAS 912-60-7 AP...
-
Tetracaine Hydrochloride CAS 136-47-0 API USP S...
-
Valsartan CAS 137862-53-4 Assay 98.0~102.0% API...
-
Telmisartan CAS 144701-48-4 Assay 99.0%~101.0% ...


